Technology
Affinity Separation, characterized by high selectivity as well as gentle and “green” processing conditions, is widely applied for isolation of high value biopharmaceutical proteins like monoclonal antibodies and therapeutic enzymes. However, the current affinity chromatography technologies are high-cost technologies, too expensive to use in e.g. high-volume food applications.
With the new ChimerAds technology, combined with highly specialized mixed-mode adsorbents, Lihme Protein Solutions provide cost-efficient use of Affinity Separation in a Dynamic Bed Adsorption format, enabling protein capture solutions for the global protein markets within food, healthcare and biopharma.
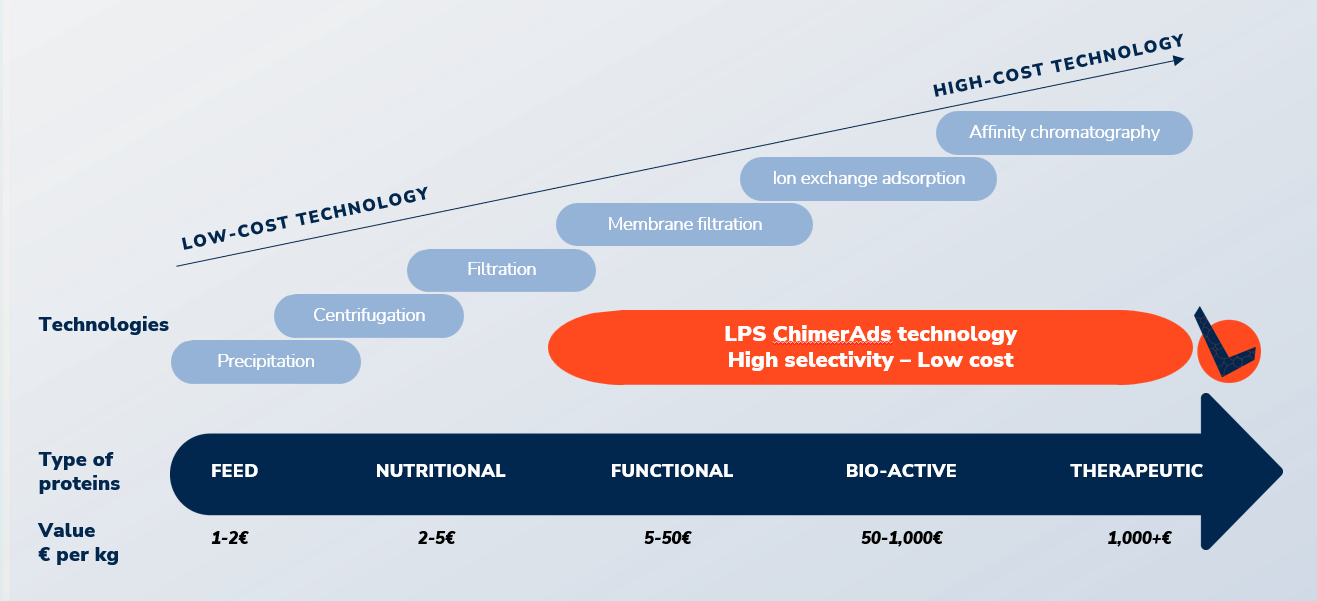
With our unique Dynamic Bed Adsorption technology, ChimerAds, we now bring value out of raw materials and side-streams in the form of new protein ingredients that so far haven’t been accessible (or profitable) by the classical separation techniques
Our ligand tool box contains the classical ion exchange principles as well as unique and highly selective mixed-mode ligands having combined hydrophobic and ionic characteristics to enable protein capture from dilute and salt containing raw materials.
Lihme Protein Solutions work closely with our clients tayloring final product features for specific applications and market needs.

The ChimerAds Technology integrates well with current industrial scale operations, such as precipitation steps and membrane filtration, to provide efficient solutions achieving high productivity and high selectivity in one combined separation process.
The ChimerAds technology is designed to require a minimum of specialized equipment in order to minimize capital investments and ease the fitting into existing industrial environments.
ChimerAds opens a wide range of opportunities for optimization of process conditions to achieve products of specific composition, functionality and yield.