Brydehusvej 30 L
DK-2750 Ballerup
Denmark
VAT: DK31286204
Lihme Protein Solutions © 2024 • All rights reserved
Bovine lactoferrin (bLf) is commercially available, but the quality varies greatly among manufacturers. The current industry practice is to isolate lactoferrin from milk or whey by ion-exchange chromatography followed by membrane filtration. This process is not necessarily able to effectively remove other minor components and endotoxins, and more steps may be needed (Perraudin & De Valck, 2020).
However, Lihme Protein Solutions has developed a solution where highly specific adsorbent, combined with our ChimerAds technology, isolates a very pure lactoferrin in few steps.
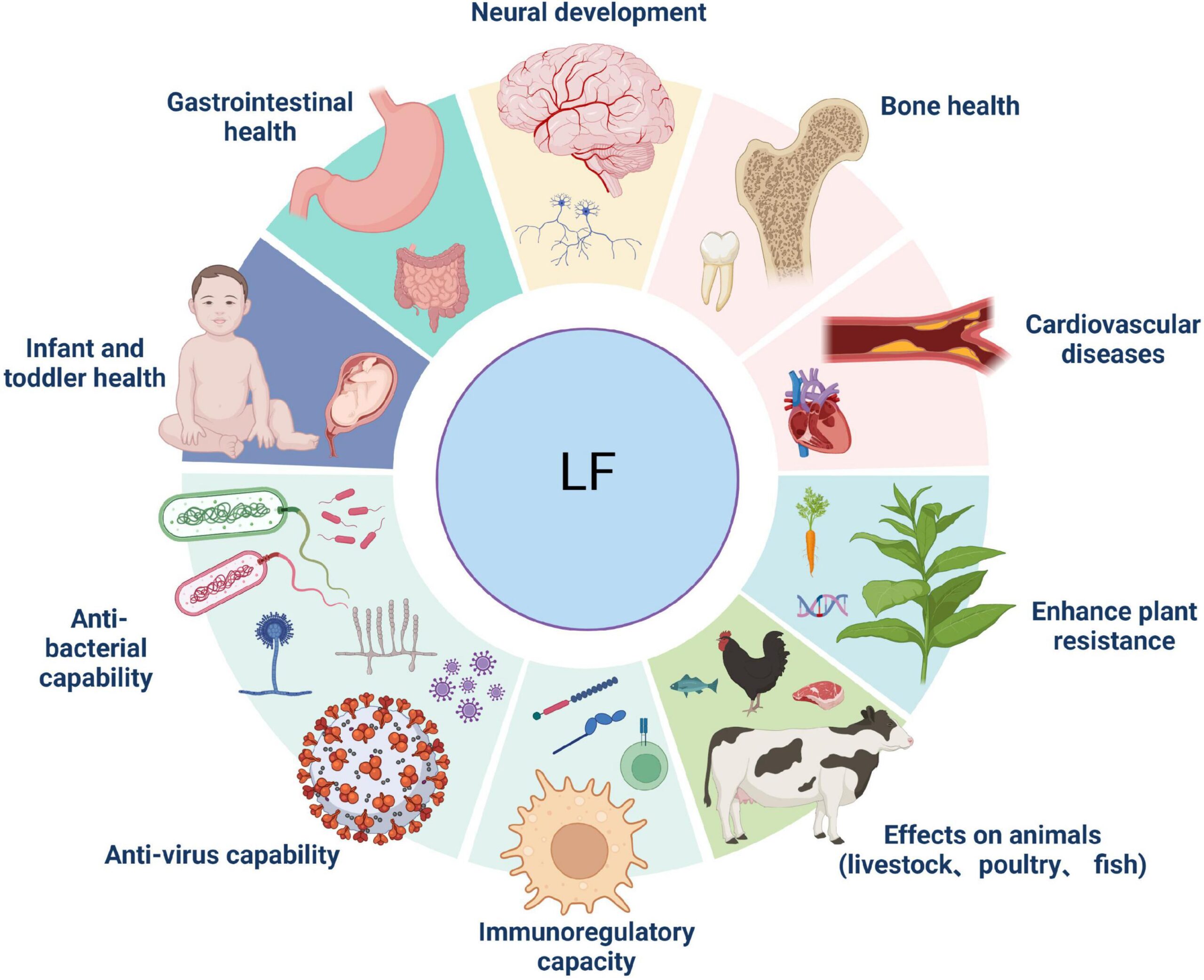
Lactoferrin is an 80-kDa iron-binding glycoprotein that belongs to the transferrin family. This multifunctional protein is found in secretions of mammals, most abundant in human colostrum (~7 g/L) and mature human milk (~1 g/L) and to a lesser content in bovine colostrum (~1.5 mg/L) and mature bovine milk (~0.5 mg/L).
The function of lactoferrin is due to its ability to sequester iron and to interfere with cellular receptors of pathogenic microorganisms.
Due to its multifunctional character and great resemblance to its human counterpart, bovine lactoferrin has a significant commercial appeal, not only in infant formulas but also for maintaining human health.
The health benefits of lactoferrin includes immunomodulating properties, antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal activities, anti-inflammatory activities, and iron regulation.
Brydehusvej 30 L
DK-2750 Ballerup
Denmark
VAT: DK31286204
Lihme Protein Solutions © 2024 • All rights reserved