Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs)
Our ChimerAds technology, combined with highly specialized adsorbents, provides cost efficient affinity separation in a dynamic bed adsorption format, enabling mAb capture platforms for the biopharmaceutical industry

Purification of mAbs
Monoclonal antibodies are used in modern-day medicine, both for diagnosis and as targeted drug therapy, see box below.
Purification of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) involves isolation from cell culture supernatants or ascites fluid, seeking high monomer purity and low endotoxin levels.
In the biopharmaceutical industry the majority of downstream purification processes for mAbs involve Protein A-based packed bed chromatography followed by one or two more chromatographic steps for polishing. The application of our dynamic bed adsorption technique, ChimerAds, could revolutionize the commercial mAb purification processes with respect to process economics, yield and purity.
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) – the proteins
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are laboratory-produced immunoglobulins either produced by recombinant genetic engineering or by cloning specific B-cells that release homogenous antibodies.
Both methods produce a single antibody clone in large volumes and with a pre-selected affinity for one specific antigen epitope.
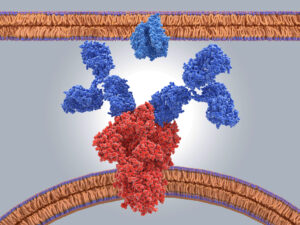
mAbs are mostly IgG’s. IgG molecules are large globular proteins made of two identical gamma heavy chains of about 50 kDa and two identical light chains of about 25 kDa. The resulting 150-kDa tetramer has two identical halves forming a Y-like shape where each end of the “fork” contains an identical antigen binding site.
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) – the use
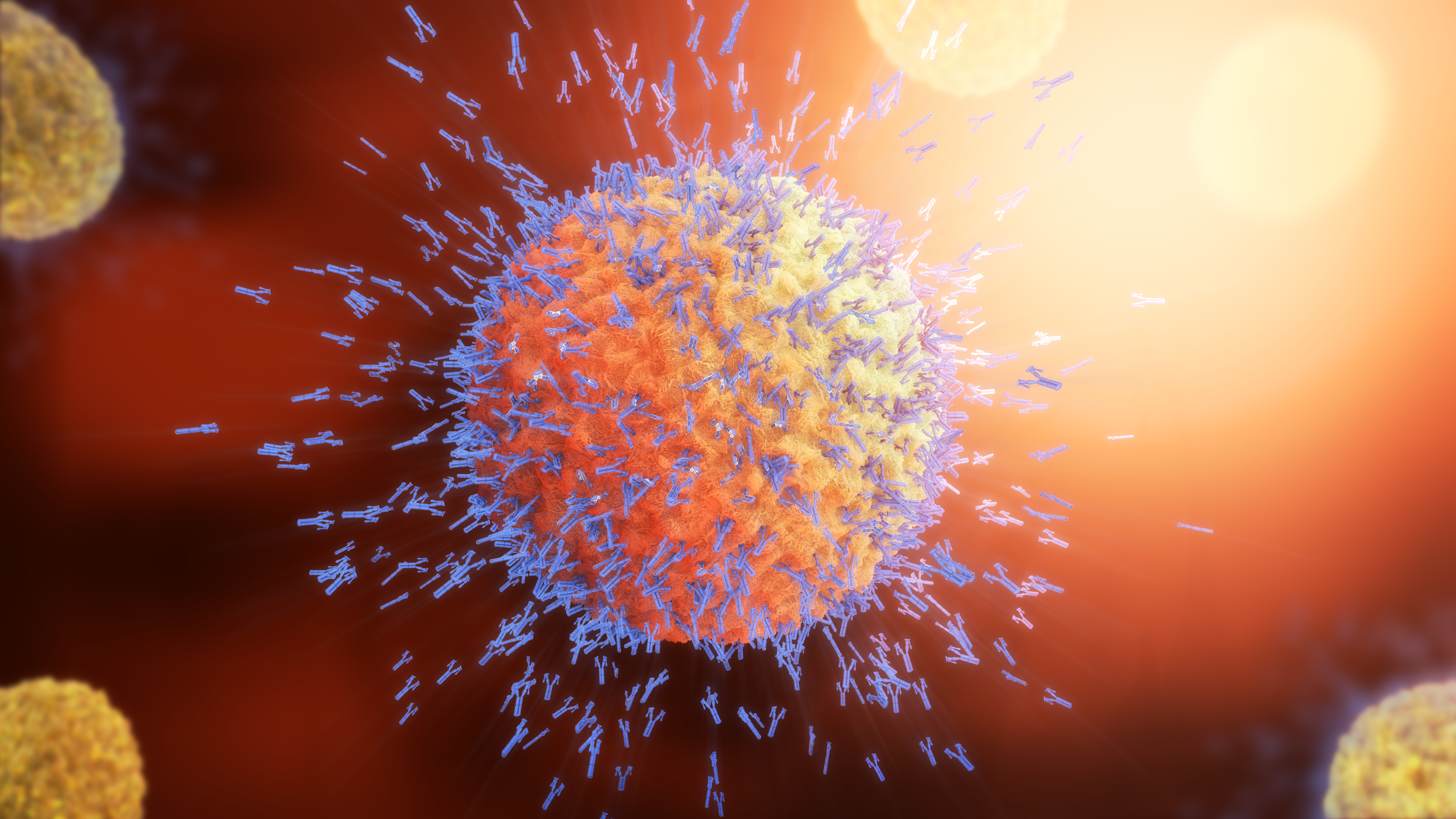
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are used as highly individualized therapeutics for a variety of cancers and autoimmune diseases. The therapeutic mAbs act through multiple mechanisms, such as blocking of targeted molecule functions or by modulating signalling pathways. An example is seen in one kind of targeted cancer drug therapy where the mAbs recognize and find specific proteins (antigens) on cancer cells and cause the cancer cells to die (apoptosis).
mAbs are also used in therapies for various viruses, such as COVID-19 and HIV/AIDS, however, especially concerning the latter, it is often challenging because of the relatively high mutation rate of the virus.
mAbs are also used in medical diagnostic tests.
